Cybersecurity has long been reactive, often addressing vulnerabilities after deployment. But in the era of cloud-native applications, this approach is no longer sufficient. Shifting security left—embedding it into the earliest stages of development—enables organisations to identify and mitigate risks before they impact production.
The software supply chain, which includes source code, build systems, and container images, is a primary target for attackers. By integrating scanning tools directly into development workflows, organisations can meet NIS 2 and DORA requirements for proactive risk management and secure software delivery pipelines.
Why Shifting Left Matters
The earlier a vulnerability is detected, the less costly and time-consuming it is to fix. Shifting security left aligns perfectly with DORA, which emphasizes resilience and proactive measures. For example, source code scanning during development can catch issues before they propagate downstream, reducing risks and maintaining operational continuity.
How to Shift Left with Aqua CNAPP
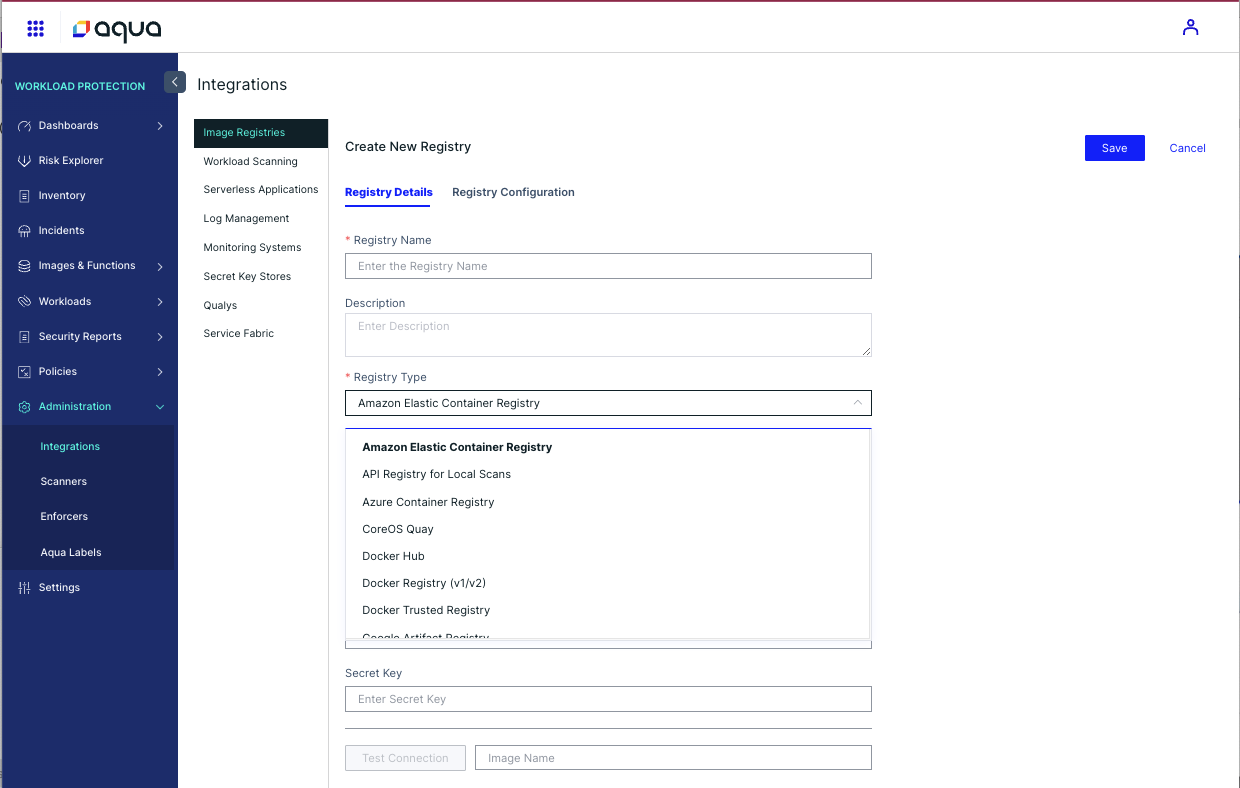
- Bulk Scanning of Registries:
- Connect Aqua to all source code repositories and container registries.
- Set up scheduled scans to ensure every new artifact is analysed for vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and secrets.

-
Continuous Monitoring:
- Leverage Aqua’s automated pull schedules to keep scans up-to-date as new code is committed or images are pushed to the registry.
-
Developer Enablement:
- Integrate scanning results directly into developers’ workflows using CI/CD tools. Aqua’s feedback mechanisms provide actionable insights, enabling developers to fix issues quickly without leaving their environments.
-
Establish Baselines:
- Use initial scan results to create a baseline of vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. Prioritise fixes for critical issues while monitoring progress over time.
Practical Example: Automating Scans in CI/CD Pipelines
A typical Aqua configuration in a CI/CD pipeline, using Github Actions in this instance, might look like this:
name: allthingsclowd APP
on:
push:
branches:
- main
pull_request:
branches:
- main
workflow_dispatch:
env:
DOCKER_REPOSITORY: allthingscloud # name of Docker Hub ID
IMAGE_NAME: allthingsclowd-app
IMAGE_TAG: ${{ github.run_number }} # $GITHUB_RUN_NUMBER
jobs:
CI-Code:
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Integrity pipeline
uses: aquasecurity/pipeline-enforcer-action@main
with:
aqua-key: ${{ secrets.AQUA_KEY }}
aqua-secret: ${{ secrets.AQUA_SECRET }}
verbose: true
- name: Aqua code scanning(SCA,IaC, Secrets/Sensitive Data, Pipeline file and SAST)
uses: docker://aquasec/aqua-scanner
with:
args: trivy fs --scanners config,vuln,secret --sast --reachability --package-json .
# To customize which severities to scan for, add the following flag: --severity UNKNOWN,LOW,MEDIUM,HIGH,CRITICAL
# To enable SAST scanning, add: --sast
# To enable npm/dotnet non-lock file scanning, add: --package-json / --dotnet-proj
env:
AQUA_KEY: ${{ secrets.AQUA_KEY }}
AQUA_SECRET: ${{ secrets.AQUA_SECRET }}
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ github.token }}
TRIVY_RUN_AS_PLUGIN: 'aqua'
CI-Build:
needs: CI-Code
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Integrity pipeline
uses: aquasecurity/pipeline-enforcer-action@main
with:
aqua-key: ${{ secrets.AQUA_KEY }}
aqua-secret: ${{ secrets.AQUA_SECRET }}
verbose: true
- name: Build application
run: echo Application has been succesfully built
- name: Build image container
run: |
sudo docker build -t $DOCKER_REPOSITORY/$IMAGE_NAME:$IMAGE_TAG .
- name: Login to Aqua Registry
uses: docker/login-action@v1
with:
registry: registry.aquasec.com
username: ${{ secrets.AQUA_REGISTRY_USERNAME }}
password: ${{ secrets.AQUA_REGISTRY_PASS }}
- name: Scanning container image
run: |
docker run --rm -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock registry.aquasec.com/scanner:2022.4 scan --register --registry "CI/CD_graham_images" --host ${{ secrets.AQUA_HOST }} --local $DOCKER_REPOSITORY/$IMAGE_NAME:$IMAGE_TAG --token ${{ secrets.AQUA_TOKEN }} --layer-vulnerabilities --no-verify --html > .github/workflows/scan-output.html
- name: Docker Login & Push
run: |
echo "${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}" | docker login -u ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }} --password-stdin
docker push $DOCKER_REPOSITORY/$IMAGE_NAME:$IMAGE_TAG
docker tag $DOCKER_REPOSITORY/$IMAGE_NAME:$IMAGE_TAG $DOCKER_REPOSITORY/$IMAGE_NAME:latest
docker push $DOCKER_REPOSITORY/$IMAGE_NAME:latest
- name: SBOM Generation
run: |
export BILLY_SERVER=https://billy.codesec.aquasec.com
curl -sLo install.sh download.codesec.aquasec.com/billy/install.sh
curl -sLo install.sh.checksum https://github.com/argonsecurity/releases/releases/latest/download/install.sh.checksum
if ! cat install.sh.checksum | sha256sum ; then
echo "install.sh checksum failed"
exit 1
fi
BINDIR="." sh install.sh
rm install.sh install.sh.checksum
./billy generate \
--access-token "${{ github.token }}" \
--aqua-key "${{ secrets.AQUA_KEY }}" \
--aqua-secret "${{ secrets.AQUA_SECRET }}" \
--artifact-path "$DOCKER_REPOSITORY/$IMAGE_NAME:$IMAGE_TAG"
CD-Deploy_to_dev:
needs: CI-Build
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: interity Pipeline
uses: aquasecurity/pipeline-enforcer-action@main
with:
aqua-key: ${{ secrets.AQUA_KEY }}
aqua-secret: ${{ secrets.AQUA_SECRET }}
verbose: true
- name: Setting K8s context
uses: azure/k8s-set-context@v3
with:
method: kubeconfig
kubeconfig: ${{ secrets.KUBE_CONFIG_GRAZ }}
context: graz-dev-context
- name: Deploying to Dev
run: |
export IMAGE_CONTAINER="docker.io/$DOCKER_REPOSITORY/$IMAGE_NAME:$IMAGE_TAG"
sed -e "s#{{ IMAGE_CONTAINER }}#$IMAGE_CONTAINER#g" "./manifests/dev/deployment.yaml" |
kubectl apply -f -
kubectl apply -f ./manifests/dev/service.yaml
This automation ensures that every build is scanned for high-severity vulnerabilities, providing immediate feedback to developers.
Summary
Shifting security left transforms the software supply chain from a vulnerability hotspot into a fortress of resilience. By embedding Aqua’s scanning tools into your workflows, you not only improve security but also align with DORA’s proactive approach to operational resilience. The earlier you act, the stronger your defences.

Leave a comment